Datasets
Contents
Introduction
The Dataset concept allows you to define sets of data from different tables and export this data in one step. Datasets are especially useful for managing reference data for a module, for example tax rates or default data in new tables added by a module. The reference data is packaged, distributed and installed together with the program code implementing the module.
The content of a Dataset is defined by its Dataset Tables and Dataset Columns. The first defines which tables are exported, the second one which columns from those tables are exported.
Datasets can be defined at System, Organization, or Client/Organization levels. System-level datasets are applied when the module containing them is installed in the system. Their data is system-level.
Organization-level datasets can be applied in Initial Organization Setup (when creating a new organization), or can also be applied to an existing organization using the Enterprise Module Management window. They contain Organization level information.
Client/Organization-level datasets work like Organization-level datasets, but can also be applied on Initial Client Setup when creating a new client. They contain Organization/Client level information.
Main Concepts
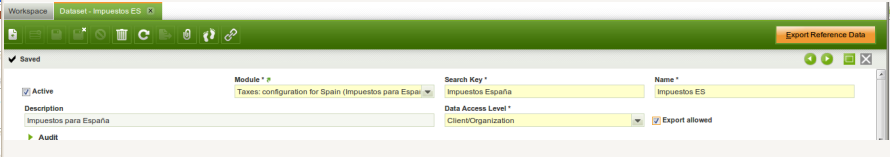
Dataset
A Dataset is a grouping of different tables (entities) which are exported together. Datasets are defined through the Dataset menu in the Application Dictionary. Below is an example of a Dataset.
Some important things to note:
- A Dataset belongs to a module, so modules can add new datasets to an Openbravo instance.
- Data Access Level: filters the tables which can be selected for this dataset, only tables with the set data access level can be included in the data set (see here for more information on data access level).
If the export allowed column is flagged then an export button is displayed. When clicking this button the data is exported to the modules directory of the module to which the Dataset belongs:
DatasetTable
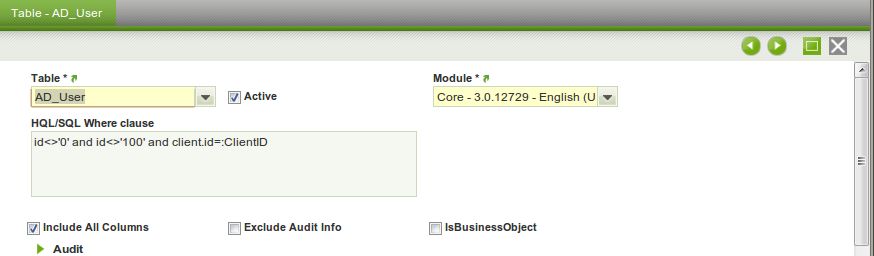
The DatasetTable defines which data of one table is to be exported. It defines both the records (through a where clause) and the columns per record. A Dataset should have one or more Dataset Tables, a Dataset Table belongs always to exactly one Dataset.
Some important aspects:
- A Dataset Table has a module, so you can add a new Dataset Table to an existing Dataset (of another module).
- The SQL where clause is a HQL where Clause. The properties which can be used in the clause are the properties of the table (= entity) of the DatasetTable. See the next subsection for more information.
- Include all columns: if flagged all columns are exported, except the ones excluded in the DataSet Column, if not flagged then the DatasetColumn definition is used.
- Exclude Audit Info: only relevant if include all columns is flagged, in that case this field can be used to exclude audit info. In most situations, it makes sense to activate this flag, as audit info (information about which user created and updated every record, and in which date this happened) is most of the times irrelevant, when exporting business data to a dataset which is meant to be generic and used in several different systems.
- IsBusinessObject: if flagged then also the 'child-records' of the table are exported, for example if the Dataset Table is defined for the C_Order table and this field is flagged then also the related C_OrderLines are exported. See here for more details on how business object structures are defined.
DatasetTable where clause
To select specific objects from the table to be included in the data set it is possible to define a where clause in the DatasetTable. The SQL where clause is a HQL where Clause. The properties which can be used in the clause are the properties of the table (= entity) of the DatasetTable. The entity and property names gives an overview of all properties by their entity. There are two standard parameters which can be used in the HQL clause:
- ClientID: denoting the current client of the user exporting the data
- moduleid: the id of the module for which data is exported
The syntax of using these parameters in the where-clause is the same as for named parameters in HQL in general.
Here are some examples of where clauses:
- client.id = :ClientID, export all objects from the current client
- client.id = '0', export only objects from the zero client
- processed = true and chargeAmount > 0, export only objects which have been processed and for which the charge amount > 0
- client.id in ('0', '1000000'), select all objects with a client 0 or 1000000
- name like '%Product%', select objects with a name which contains the string Product
The clause can contain inner-selects and other more advanced HQL features. However, order-by, group-by and having clauses are not supported, so the content of this field should just be the where-clause and nothing more.
DatasetColumns
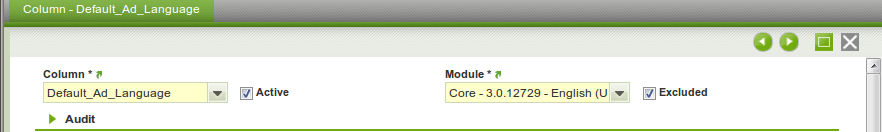
The Dataset Columns defines the columns/properties which are exported for a certain business object (= Dataset Table). A Dataset Column always belongs to one Dataset Table, and a Dataset Table can have zero or more Dataset Columns. The Dataset Column concept can be used in two ways:
- check the 'Include all columns' in the Dataset Table and define exclusions in the Dataset Column
- do not check the 'Include All Columns' in the Dataset Table and define the exact Columns to export in the Dataset Column
The main fields:
- A Dataset Column has a module, so you can add a new Dataset Column to an existing Dataset Table (of another module).
- Excluded: if flagged then this column is defined not to be exported.
Usage of Datasets
The main purpose of Datasets is to define reference data for modules. This function is explained in more detail here.
To export a dataset, it is very important to follow these steps:
- First click on the "Export Reference Data" button in the Dataset window. This will export the dataset contents to an xml file, and will also generate the checksum of this dataset.
- Then, execute "ant export.database" to export the checksum information to the module source data.
After this, you can do "ant package.module -Dmodule={module java package}" to package your module, which now will include the contents of the dataset.
The reference data is inserted when a module is applied (build and installed). Or can be imported separately (see next section).
Data ownership
Data defined by a dataset is owned by this dataset. This means when there is an update of this dataset, any change on this data will be overwritten again to match the definition in the new version of the dataset.
Starting from PR15Q2, it is possible to mark a dataset as Default Values Data Set. Having this flag makes the dataset not to take ownership of the data it inserts but moving this ownership to the instance. So new records provided by the dataset are inserted, even in newer versions of this dataset, but any changes done in the instance will be preserved. Note in case a record provided by one of these datasets is deleted from the instance, it will be recovered back in the next update, the correct way of getting rid of undesired records is by marking them as inactive.
Importing Reference Data on Organization level
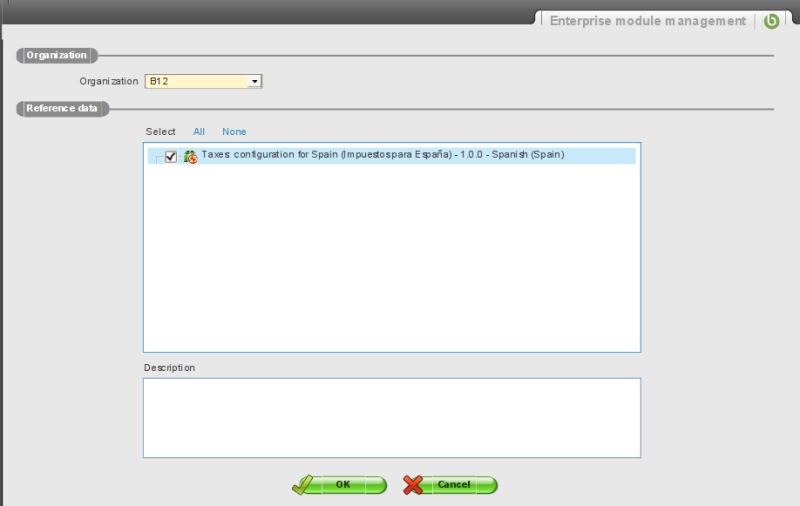
The module reference data can be imported into an organization using the Enterprise Module Management function. It is available in the menu here: General Setup > Enterprise > Enterprise module management > Enterprise module management.
In this list, only the relevant modules containing datasets will be shown. This means that if a dataset hasn't changed from the last time it was applied to the selected organization, it will not be shown.
Select the organization and the module from which to import the reference data into the organization. Then press ok. After a while the result page is displayed:
If a dataset is defined as Organization/Client level, then it can also be imported when using the Initial Client Setup utility to create a new client.