Template:ManualDoc:FDE2329ABCAA84D5F99B59043CFFFE454
An Organization is an enterprise of a Client. A client can have at least one or even more than one organization as the way of configuring different types of enterprises models.
Overall organizations can be:
- independent legal entities with a different Tax ID number
- enterprise groups with the aim of getting aggregated figures for the group
- or business areas of the client such as departments
Besides organizations can be structured:
- by country or region
- by area or function
- and so on so forth, according to the enterprise model needs.
All of the above provides an insight about the different scenarios which need to be covered while modelling the enterprise.
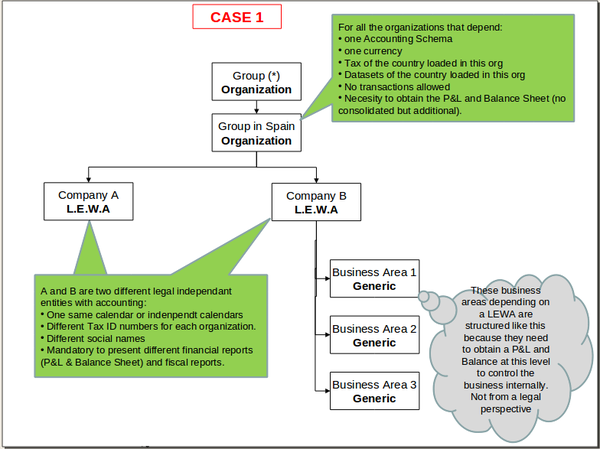
There could be organizations which require to share master data such as business partners and product while having its own chart of account, taxes, financial reporting and transactional data. That could be the case of independent legal entities belonging to the same enterprise group.
There could be organizations sharing master data and even the same chart of accounts. That could be the case of divisions or departments within the same independent legal entity.
There could be organizations created with the aim of just grouping data, for which its own transactional data is not required.
All of the above is possible due to the fact that there are different types of Organizations, see below section, and besides organizations can be structured in a hierarchical way:
- At the highest level of the tree, there is an organization named (*).
- (*) organization is created at the same time that the system client is created, and it is shared among the different client/s in the system.
- Master data created at (*) organization level is accessible for all the organization beneath it
- (*) organization is not an independent legal entity therefore transactional data is not allowed.
- Every organization created later on will be created below (*) organization.
- At a lower level of the tree, there can be parent organization/s which can have child organization/s beneath it/them.
- Master data such as business partners and products created at parent organization level is accessible for all the child organization/s beneath it.
- At the lowest level of the tree, there can be child organization/s with no organizations beneath it/them.
- Master data such as business partners and products created at child organization level will not be accessible for the rest of the child organizations if any.
Initial Organization Setup
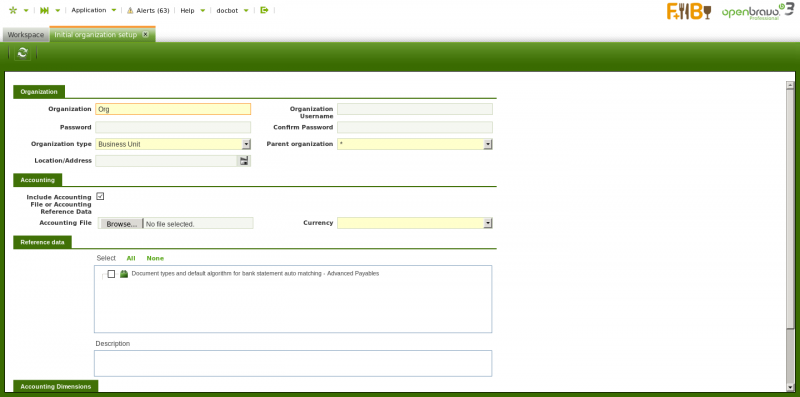
As already mentioned Organizations are created by running the Initial Organization Setup process and not only that, once an organization has been created it must be set as "Ready" in the Organization window
As shown in the image above an organization can be created by providing below relevant data:
- the name of the organization
- the name of the user of the organization
- Openbravo creates a new user and a new role which only have access to the newly created organization.
- This user can be later on changed by assigning new roles to it.
- And the role can also be later on changed by assigning new organizations to it.
- Openbravo creates a new user and a new role which only have access to the newly created organization.
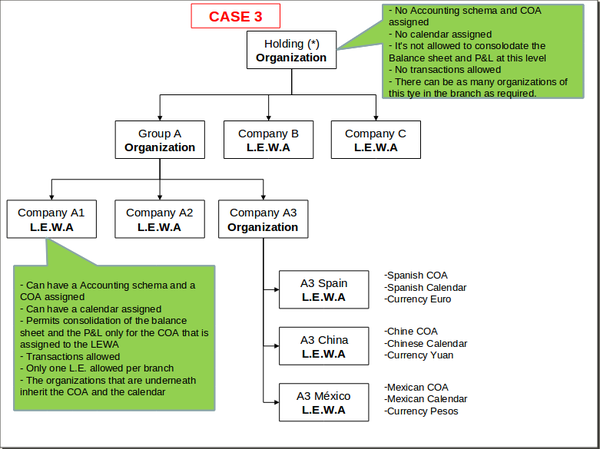
- the organization type. The options available are:
- Organization - an organization which is not a legal entity and does not allow transactional data entering.
- This type of organization allows the creation and configuration of master data to be shared among a group of organizations of any type belonging to it, for instance Business Partners, Chart of Accounts, etc.
- It does not require general ledger as it does not allow entering transactions but it can have a given General Ledger configuration to be shared among the organizations underneath
- The accounting periods can not be opened and closed independently at its level.
- And there could be as many organizations type "organization" in a branch as required.
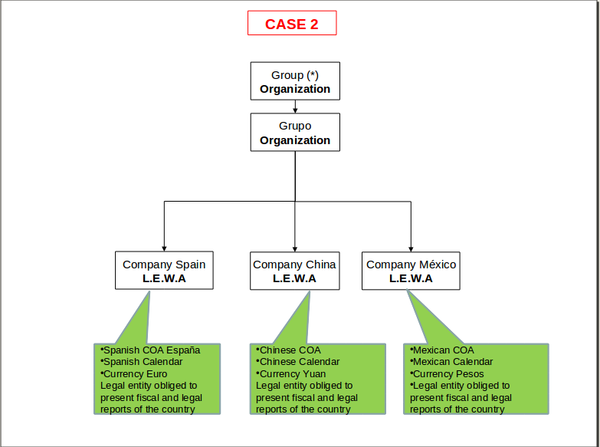
- Legal with accounting - an independent legal entity with a unique Tax Id number which requires accounting, therefore:
- this organization requires General Ledger and therefore an Account Tree or Chart of Accounts, as well as a Fiscal Calendar because the accounting periods can and must be opened and closed at its level.
- This organization type allows the "consolidation" of the Balance Sheet and P&L reports only for the Chart of Accounts it has assigned.
- Transactions are allowed for this organization type.
- And finally, there can only be one legal entity per tree branch, therefore the organizations underneath inherit the General Ledger configuration and the Fiscal Calendar of the legal with accounting organization.
- Legal without accounting - an independent legal entity with a unique Tax Id number which does not require accounting because it is managed in a separated system, therefore:
- this organization type does not need general ledger neither a chart of accounts and will not support financial reports at its level.
- Transactions are allowed for this organization type. Transactions which will not be posted to the ledger.
- It can not have another legal entity in an upper/lower level of the enterprise tree structure.
- Generic - an organization which is not a legal entity but must belong to a legal entity placed at an upper level in the organization tree structure. For instance departments or divisions withing an organization or legal entity.
- There could be as many generic organizations as requires per tree branch but always under a legal entity.
- This organization type allows transactional data entry, can have its own general ledger configuration and can inherit the general ledger configuration of the legal entity with accounting they belongs to.
- The accounting periods can not be opened and closed independently at its level.
- Organization - an organization which is not a legal entity and does not allow transactional data entering.
- the parent organization. While creating an organization it is possible to select the organization to which the organization being created will belong to. The parent organization would need to be set as "Summary".
- A generic organization can not be the parent organization of a legal entity organization but the other way around.
- the organization location/address
- and the organization currency
Besides:
- There is a checkbox named "Include Accounting" which allows to select for an organization:
- an accounting csv file in the field "Accounting File"
- or a Chart of Accounts module reference data in the section "Reference Data". Reference data coming from extensions modules is master data such as Taxes, Chart of Accounts, etc to be applied from the already installed modules.
- This action creates:
- a General Ledger configuration which is automatically linked to the Organization being created
- and an Account Tree or Chart of Accounts which is also linked to the Organization being created
- This step does not create a Fiscal Calendar as the Initial Client Setup process does, because Fiscal Calendars needs to be created ad hoc for the "Legal with Accounting" Organizations for which "Allow Period Control" feature is going to be enabled.
- Note that this step does not imply to manage accounting within an organization but just to include an accounting file or an accounting reference data in an organization.
Accounting management relies on the organization type being created.
- It is not mandatory to select "Include Accounting" checkbox while creating a legal entity with accounting organization for instance because:
- a legal entity with accounting can inherit the client chart of accounts
- or later on both the Chart of Accounts and the General Ledger configuration can be created manually and be linked to the organization.
- if the checkbox "Include Accounting" is selected it is possible to select for the organization being created below dimensions to be used while posting organization's documents to the ledger:
- mandatory accounting dimensions such as "Business Partner" and "Product" and not mandatory accounting dimensions such as "Project" and "Sales Region" while creating an Organization in a "Client" which does not centrally maintain the accounting dimensions.
In that case the dimensions selected in here will all be listed in the dimensions tab of the organization's general ledger configuration, therefore will be available just for that organization. - additional accounting dimensions such as "Project" or "Campaign" while creating an Organization in a "Client" which centrally maintains the accounting dimensions.
Once more the dimensions selected in here will be listed in the dimensions tab of the organization's general ledger configuration, therefore will be available just for that organization.
- mandatory accounting dimensions such as "Business Partner" and "Product" and not mandatory accounting dimensions such as "Project" and "Sales Region" while creating an Organization in a "Client" which does not centrally maintain the accounting dimensions.
It is possible to apply reference data such as:
- Document types and default algorithm for bank statements auto-matching, this one is similar to the previous one but for specific financial flows such as Payment Outs, Payment In and Financial Accounts.
- or reference data such as master data or configuration data (i.e. tax setup) created for Openbravo extension modules.
Finally, it is important to remark that:
- Each organization, not matter the type, can have it's own general ledger configuration/s and currency/ies (apart from the one inherit from its parent) if it is configured to be that way for the Organization
- A calendar is mandatory just for the legal entities with accounting. This organization type is the only one which can have a calendar assigned, the rest can inherit it.
- Financial reports are run by general ledger configuration and therefore by currency as each general ledger configuration has only one currency allowed.
- Financial Reports such as the Balance Sheet and the P&L as well as Tax Reports can only be created at the level of Legal Entity with accounting.
- Rest of reports such as sales, procurement and warehouse reports can be launched for any organization type.
- A general ledger configuration should not be assigned to the (*) organization because that one will then be shared by all the organizations underneath.
Examples
1. Openbravo Demo Data:
Openbravo includes a demo data for demonstration purpose which includes an "Enterprise Model" composed by a set of organizations.
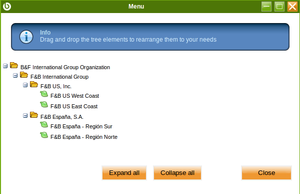
- An organization type "Organization" named F&B International Group.
- This organization is not a legal entity and it does not allow transactions
- This organization allows the creation and configuration of master data to be shared among a group of organizations beneath it
- Two "legal entities with accounting" named "F&B España" and "F&B US" that belongs to F&B International Group.
- Below the legal entities with accounting organizations there are four "Generic" organizations, which are not legal entities but belong to a legal entity and besides allow transactional data entry:
- F&B US West Coast
- F&B US East Coast
- F&B España - Region Norte
- F&B España - Region Sur
2. How to create each Organization type:
The basic variables to take into account while creating an organization of the type "Organization" are:
- Organization Type = Organization
- Include Accounting = Yes
If the accounting configuration at this level needs to be shared by all the organizations underneath the one being created. - Accounting Dimensions = Business Partner, Product and Project
The basic variables to take into account while creating an organization of the type "Legal with accounting" are:
- Organization Type = Legal with accounting
- Include Accounting = Yes
- Accounting Dimensions = Business Partner, Product and Project
The basic variables to take into account while creating an organization of the type "Legal without accounting" are:
- Organization Type = Legal without accounting
- Include Accounting = No
The basic variables to take into account while creating an organization of the type "Generic" are:
- Organization Type = Generic
- Include Accounting = Yes
If this organization requires its own accounting configuration besides the inherited one, otherwise include accounting = No - Parent organization = should be a "Legal with Accounting" organization.
3. Enterprise Models examples: